Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kikuchi, Shin; Sakamoto, Kan*; Takai, Toshihide; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2020-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/09
In a postulated severe accidental condition of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), eutectic melting between boron carbide (B C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B
C) as control rod element and stainless steel (SS) as control rod cladding or related structure may occur. Thus, behavior of B C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B
C-SS eutectic melting is one of the phenomena to evaluate the core disruptive accidents in SFR. In order to clarify the kinetic feature of B C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B
C-SS eutectic melting process in the interface, the thinning test for SS crucibles using the pellets of B C or SS with low B
C or SS with low B C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B
C concentration were performed to obtain the rate constant with dependence of B C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B
C concentration against SS. It was found that the rate constants of eutectic melting between SS and SS low B C concentration were smaller than that of B
C concentration were smaller than that of B C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B
C-SS in the high temperature range. Besides, the rate constant of eutectic melting between SS and B C containing SS became small when decreasing the B
C containing SS became small when decreasing the B C concentration against SS.
C concentration against SS.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 62(6), p.350 - 355, 2019/06
Thermal oxidation of Si substrate is an indispensable process for the Si device fabrication. However, the influence of oxidation induced strain cannot be ignored for thin films. Synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy was used as a method to measure simultaneously oxidation induced strain and oxidation rate. It was found that the acceleration of interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain was observed for the rapid thermal oxidation. The results can be explained by the model in which point defects caused by strain become reaction sites at the SiO /Si interface.
/Si interface.
Ito, Hiroto*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Tanaka, Yoichi*; Nishihara, Satomichi*; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-012, 42 Pages, 2018/10
Chemical composition of fission products transported in nuclear facilities in severe accidents is controlled by slower chemical reaction rates, therefore, it could be different from that evaluated on the chemical equilibrium assumption. Hence, it is necessary to evaluate the chemical composition with reaction kinetics. On the other hand, databases applicable to the analysis of nuclear facilities have not been constructed because knowledge of reaction rates of complex chemical reactions in severe accidents is currently limited. Accordingly, we have developed the CHEMKEq code based on a partial mixed model with chemical equilibrium and reaction kinetics to decrease uncertainties of the chemical composition caused by the reaction rate. The CHEMKEq code, under mass conservation law, firstly evaluates chemical species obeying the chemical equilibrium model, and then, relatively slow reactions are solved by the reaction kinetics model. Moreover, the CHEMKEq code has a multiplicity of use in evaluations of chemical composition because general chemical equilibrium and reaction kinetics models are also available and databases required to calculation are external file formats. This report is the user's guide of the CHEMKEq code, showing models, solution methods, structure of the code and calculation examples. And information to run the CHEMKEq code is summarized in appendixes.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Inoue, Masao; Hino, Ryutaro; Ogawa, Toru
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2014/10
Since seawater has been used as a coolant for reactors and spent fuel pools in broken reactor buildings at Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident, radioactive contaminated water emitted following the accident has contained salt content of seawater at high concentrations, different from that at TMI-2 accident. Radiolysis of seawater leading to hydrogen generation and corrosion has been simulated and reported by several groups. However, the proposed radiolysis models cannot be always applied to water radiolysis at the wide range of salt concentrations present in the NPS, mainly because primary yields of radiolysis products of water and radiation-induced reactions are dependent on the salt concentration. In this study, the radiolytic behavior in diluted and concentrated systems of seawater was considered on the basis of results in steady state and pulse radiolysis experiments, in which the above salt effects were demonstrated from the obtained results.
Ueki, Yuji; Seko, Noriaki
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 53, 2014/03
no abstracts in English
Abe, Hitoshi; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(1), p.10 - 21, 2007/03
In MOX fuel fabrication facility, zinc stearate will be added into the MOX powder as addition material. If the material is added in large excess by miss operation, criticality characteristics of the MOX fuel would be influenced because it has neutron moderation effect. If criticality condition should be induced by the excess addition, physical variations, such as melting and pyrolysis of the material, must be caused by the fission energy and dynamic characteristics of the MOX fuel must be affected. To contribute quantitative evaluation of the dynamic characteristics, thermal properties data such as exo/endothermic calorific values, reaction rates, etc. with the respective physical variations and release behavior of pyrolysis gas were measured. It was found the exo/endothermic behavior with rinsing temperature of the material could be divided into six regions and rapid pressure rise caused by the pyrolysis reaction over about 400  C. Furthermore, on the basis of the results, evaluation model for the thermal properties under the criticality condition was also investigated.
C. Furthermore, on the basis of the results, evaluation model for the thermal properties under the criticality condition was also investigated.
Mukai, Masayuki; Tanaka, Tadao; Yukawa, Kazuhiko; Suryantoro*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu, 12(1-2), p.41 - 51, 2006/03
To evaluate radionuclides migration through geologic media coexistent with colloids in groundwater, a model has been coded. To evaluate an applicability of four models to colloid transport through porous media, breakthrough curves (BTCs) from column experiments using sand and reddish soil have been analyzed. Instantaneous equilibrium model could not explain both timings of breakthrough and reach to C /C
/C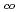 =1 concurrenyly, however 1st order kinetic reaction model successfully simulate them well. BTCs from the reddish soil column have a particular feature that shows step-wise rising pattern in response to alternately inflow of colloid. Both the instantaneous equilibrium, the 1st order kinetic reaction and filtration models could not simulate this feature, however a 1st order kinetic reaction with filtration capacity model reasonably simulates the feature. The model for colloid transport, given an important role as a part of colloidal migration model of radionuclide, has been validated on the basis of the laboratory experiments.
=1 concurrenyly, however 1st order kinetic reaction model successfully simulate them well. BTCs from the reddish soil column have a particular feature that shows step-wise rising pattern in response to alternately inflow of colloid. Both the instantaneous equilibrium, the 1st order kinetic reaction and filtration models could not simulate this feature, however a 1st order kinetic reaction with filtration capacity model reasonably simulates the feature. The model for colloid transport, given an important role as a part of colloidal migration model of radionuclide, has been validated on the basis of the laboratory experiments.
 Ni migration through crushed rock media
Ni migration through crushed rock mediaTanaka, Tadao; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Mukai, Masayuki; Maeda, Toshikatsu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Radiochimica Acta, 92(9-11), p.725 - 729, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Migration experiments of  Ni for crushed rocks, granite and tuff, were performed under the coexistent condition with a humic acid and a fulvic acid of 0-30 mg/l in concentration, which are Nordic humic substances supplied from International Humic Substance Society. Migration experiments of Ni had been performed by a column system, to investigate migration behavior of Ni through a column packed crushed rock. The Ni concentration in the effluent passed through the column was corresponding to the fractional percentage of Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution. This result suggests that the Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution was flowed out from the column without any effective interactions with the rock media. The migration behavior of Ni could be expressed by a migration model taking account of the complexation kinetics of Ni with humic substance in the aqueous phase.
Ni for crushed rocks, granite and tuff, were performed under the coexistent condition with a humic acid and a fulvic acid of 0-30 mg/l in concentration, which are Nordic humic substances supplied from International Humic Substance Society. Migration experiments of Ni had been performed by a column system, to investigate migration behavior of Ni through a column packed crushed rock. The Ni concentration in the effluent passed through the column was corresponding to the fractional percentage of Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution. This result suggests that the Ni complexing with humic substance in influent solution was flowed out from the column without any effective interactions with the rock media. The migration behavior of Ni could be expressed by a migration model taking account of the complexation kinetics of Ni with humic substance in the aqueous phase.
 ion irradiation
ion irradiationWakai, Eiichi; Ezawa, Tadashi*; Imamura, Junko*; Takenaka, Tsuyoshi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Oshima, Ryuichiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part.1), p.367 - 373, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:84.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 +C
+C H
H H+C
H+C H
H reaction and its isotopic variants
reaction and its isotopic variantsKurosaki, Yuzuru; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki
Journal of Chemical Physics, 113(10), p.4060 - 4072, 2000/09
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.85(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
JNC TN8400 2000-012, 33 Pages, 2000/04
The redox condition of near-field is expected to affect the performance of engineered barrier system. Especially, the oxygen initially existing in the pore space of compacted bentonites strongly affects the redox condition of the near-field. For assessing the influence of the oxygen, the transport parameters of it in the compacted bentonite and consumption process should be known. Therefore, following researches were conducted. In order to understand the diffusion of dissolved oxygen (DO) in compacted bentonite and to predict the effect of DO, the effective diffusion coefficients of DO in compacted sodium bentonite were measured by electrochemistry. As the results, the following relationship between the dry density of compacted sodium bentonite and the effective diffusion coefficient of DO in compacted sodium bentonite was derived: De=1.53 0.13
0.13 10
10 exp(-2.15
exp(-2.15 0.24
0.24 10
10 p) where De is the effective diffusion coefficient (m
p) where De is the effective diffusion coefficient (m s
s ) of DO in compacted sodium bentonite and
) of DO in compacted sodium bentonite and  is the dry density (kg m
is the dry density (kg m ) of compacted sodium bentonite. The oxygen concentration in the bentonite is expected to be controlled by oxidation of pyrite as impurity in the bentonite. In order to investigate the above idea, the rates of pyrite oxidation by DO in compacted sodium bentonite were estimated from the experimental data on pyrite-bentonite systems usig the obtained effective diffusion coefficient of DO. The results show that the averages of the rate constants of pyrite oxidation by DO in the bentonite for dry densities of 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2
) of compacted sodium bentonite. The oxygen concentration in the bentonite is expected to be controlled by oxidation of pyrite as impurity in the bentonite. In order to investigate the above idea, the rates of pyrite oxidation by DO in compacted sodium bentonite were estimated from the experimental data on pyrite-bentonite systems usig the obtained effective diffusion coefficient of DO. The results show that the averages of the rate constants of pyrite oxidation by DO in the bentonite for dry densities of 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2 10
10 kgm
kgm were 1.38
were 1.38 0.32
0.32 10
10 , 1.10
, 1.10 0.24
0.24 10
10 , 1.16
, 1.16 0.35
0.35 10
10 , 9.36
, 9.36 2.23
2.23 10
10 and 7.48
and 7.48 1.92
1.92 10
10 ms
ms , respectively. The relationship between the dry density (
, respectively. The relationship between the dry density ( ) and the rate constant (k') was expressed as follows: k'=3.94
) and the rate constant (k') was expressed as follows: k'=3.94 1.06
1.06 10
10 exp(-1.33
exp(-1.33 0.28
0.28 10
10
 ) ...
) ...
; Koyama, Tomozo; Funasaka, Hideyuki
JNC TN8400 2000-014, 78 Pages, 2000/03
We investigated the factors which affected the dissolution of U and Pu to the nitric acid solution with the fragmentation model, which was based on the results of dissolution experiments for the irradiated fast reactor fuels in the Chemical Processing Facility(CPF). The equation that gave the fuel dissolution rate was estimated with the condition of fabrication (Pu ratio (Pu/(U+Pu))), irradiation (burn-up) and dissolution (nitric acid concentration, solution temperature and U+Pu concentration) by evaluating these effects quantitatively. We also investigated the effects of fuel volume ratio to the solution in the dissolver, burn-up and flouring ratio of the fuel on the f-value (the parameter which shows the diffusion and osmosis of nitric acid to the fuel) in the fragmentation model. It was confirmed that the fuel dissolution rate calculated with this equation had better agreement with the results of dissolution experiments for the irradiated fast reactor fuels in the CPF than that estimated with the surface area model. In addition, the efficiency of this equation was recognized for the dissolution of unirradiated U pellet and high Pu enriched MOX fuel. It was shown that the dissolution rate of the fuel slowed down at the condition of the high U-Pu concentration dissolution by the calculation of the dissolution behavior with this equation. The dissolution of the fuel can be improved by increasing the nitric acid concentration and temperature, but from the viewpoint of lowering the corrosion of the dissolver materials, it is desirable that the f-value is increased by optimizing the condition of shearing and stirring for the improvement of dissolution.
Muroi, Masayuki*
JNC TJ8400 2000-042, 142 Pages, 2000/02
Hyperalkaline pore water of cementitious material used in TRU waste repository would react with bentonite and cause the increased porosity and the loss of the swelling and sorption ability. This work is a modelling study on bentonite-cement pore water. The possible extent of reaction between bentonite and cement pore water was simulated using the PRECIP reaction-transport code. Three cement pore fluid compositions (leachates 1,2 and 3) were reacted with a 1-D, 1m flowpath of bentonite (+ sand) at 25 and 70 C. Key minerals were allowed to dissolve and precipitate using kinetic reaction mechanism. Leachate 1 was the most aggressive fluid (highest pH, Na and K), and leachate 3 (1owest pH, Na and Ca) the least aggressive. Simulation with leachate 1 showed total removal of primary bentonite minerals up to 60 cm from the contact with cement after
C. Key minerals were allowed to dissolve and precipitate using kinetic reaction mechanism. Leachate 1 was the most aggressive fluid (highest pH, Na and K), and leachate 3 (1owest pH, Na and Ca) the least aggressive. Simulation with leachate 1 showed total removal of primary bentonite minerals up to 60 cm from the contact with cement after  1000 years. The maximum porosity increase observed was in leachate 1(up to 80-90%) over a narrow zone 1-2 cm. Simulations with all fluids showed total filling of pore with CSH minerals in a zone very close to the interface with the cement, whereas zeolites and sheet silicates formed far away. For a given leachate composition, there was little difference in the profiles at the two temperatures studied. It was suggested that bentonite alteration was not sensitive to the kinetic parameters over the conditions studied. The conceptual model chosen for the modelling study assumed that there was an unlimited amount of cement pore fluid available for reaction with bentonite so that the results of the simulations represent a conservative (pessimistic) estimate. There were a number of uncertainties associated with the modelling which relate to assumptions concerning: the kinetic mechanisms for dissolution and growth of minerals at elevated pH; evolving surface areas of minerals with time; thermodynamic data for CSH minerals, zeolites and aqueous species at high pH; the synergy between changing porosity and fluid ...
1000 years. The maximum porosity increase observed was in leachate 1(up to 80-90%) over a narrow zone 1-2 cm. Simulations with all fluids showed total filling of pore with CSH minerals in a zone very close to the interface with the cement, whereas zeolites and sheet silicates formed far away. For a given leachate composition, there was little difference in the profiles at the two temperatures studied. It was suggested that bentonite alteration was not sensitive to the kinetic parameters over the conditions studied. The conceptual model chosen for the modelling study assumed that there was an unlimited amount of cement pore fluid available for reaction with bentonite so that the results of the simulations represent a conservative (pessimistic) estimate. There were a number of uncertainties associated with the modelling which relate to assumptions concerning: the kinetic mechanisms for dissolution and growth of minerals at elevated pH; evolving surface areas of minerals with time; thermodynamic data for CSH minerals, zeolites and aqueous species at high pH; the synergy between changing porosity and fluid ...
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Fujita, Hideki*; Kubo, Hiroshi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-034, 212 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitlate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Kubo, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Hideki*
JNC TJ8400 2000-033, 95 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitrate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Akashi, Masatsune*; Fukaya, Yuichi*; Asano, Hidekazu*
JNC TJ8400 2000-015, 46 Pages, 2000/02
Difference of hydrogen generation phenomena on the surface of the Steels were not observed between carbon steel, atmospheric corrosion resisting steel and 5%-Ni steel. Rust layer was formed on these three-type of steels by steam oxidation method. And the chemical composition of the rust for the steels were basically two (2) layers structure for the previous two steels as hematite (Fe O
O ) based for the outer layer and magnetite (Fe
) based for the outer layer and magnetite (Fe O
O ) based for the inner layer. And for the last steel, it had three (3) layer in the rust as hematite (Fe
) based for the inner layer. And for the last steel, it had three (3) layer in the rust as hematite (Fe O
O ) based for the outer layer, magnetite (Fe
) based for the outer layer, magnetite (Fe O
O ) based for the intermediate layer and Ni based layer for the inner layer. These steels showed mostly same Tafel gradient in their cathodic polarization curves compare with that for no rust specimens. However, the exchange current density which reaction is assumed as a hydrogen generation reaction was largely increased. The cathodic reaction for each steels whose surface is covered by magnetite layer might be accelerated, then the corrosion rate was considered as accelerated, too.
) based for the intermediate layer and Ni based layer for the inner layer. These steels showed mostly same Tafel gradient in their cathodic polarization curves compare with that for no rust specimens. However, the exchange current density which reaction is assumed as a hydrogen generation reaction was largely increased. The cathodic reaction for each steels whose surface is covered by magnetite layer might be accelerated, then the corrosion rate was considered as accelerated, too.
Akashi, Masatsune*; Fukaya, Yuichi*; Asano, Hidekazu*
JNC TJ8400 2000-014, 22 Pages, 2000/02
Difference of hydrogen generation phenomena on the surface of the Steels were not observed between carbon steel, atmospheric corrosion resisting steel and 5%-Ni steel. Rust layer was formed on these three-type of steels by steam oxidation method. And the chemical composition of the rust for the steels were basically two(2) layers structure for the previous two steels as hematite(Fe O
O ) based for the outer layer and magnetite(Fe
) based for the outer layer and magnetite(Fe O
O ) based for the inner layer. And for the last steel, it had three(3) layer in the rust as hematite(Fe
) based for the inner layer. And for the last steel, it had three(3) layer in the rust as hematite(Fe O
O ) based for the outer layer, magnetite(Fe
) based for the outer layer, magnetite(Fe O
O ) based for the intermediate layer and Ni based layer for the inner layer. These steels showed mostly same Tafel gradient in their cathodic polarization curves compare with that for no rust specimens. However, the exchange current density which reaction is assumed as a hydrogen generation reaction was largely increased. The cathodic reaction for each steels whose surface is covered by magnetite layer might be accelerated, then the corrosion rate was considered as accelerated, too.
) based for the intermediate layer and Ni based layer for the inner layer. These steels showed mostly same Tafel gradient in their cathodic polarization curves compare with that for no rust specimens. However, the exchange current density which reaction is assumed as a hydrogen generation reaction was largely increased. The cathodic reaction for each steels whose surface is covered by magnetite layer might be accelerated, then the corrosion rate was considered as accelerated, too.
Shibata, Toshio*; *; *; Tsuru, Toru*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*
JNC TJ8400 2000-013, 38 Pages, 2000/02
None
Sumiyama, Morio*
JNC TJ8400 2000-009, 138 Pages, 2000/02
To evaluate corrosion behavior of carbon steel, a candidate materials of overpack, buried in soil for a long time, the water pipes buried in freshwater clay for a long time we digged out and the soil environment and the corrosion weight loss of pipes have been researched. From the results, a corrosion model (an empirical equation), an oxygen reduction reaction rate-determing step type, of carbon steel buried in soil was introduced. The corrosion data of under ground pipe collected by the Japan Community Gas Associations was used to increase reliability of the corrosion model equation. These data are one of researches of corrosion behavior of carbon steel buried in soil for a long time studied by at home and abroad. 38 samples buried freshwater clay were selected in 171 samples. With estimating the corrosion velocities and the soil environment factors of the above data, the maximum depth of pit corrosion was calculated by the statistical method of the extreme values using the area of overpack as the recurrent time. The correlation between the soil environment factors and the corrosion weight loss was obtained by the correlation analysis. The corrosion model of the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 of cumulative probability was compared between the under ground pipe data and the above data. On the reference data and the above data, the corrosion model equation; H = aY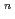 was compared with the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 cumulative probability. The data of water pipes and community gas pipes at 0.99 cumulative probability showed the reasonable values when these data were compared with the reference data. So that the model was proved as a good corrosion model m the neutral low dissolved oxygen environment.
was compared with the maximum depth of pit corrosion at 0.99 cumulative probability. The data of water pipes and community gas pipes at 0.99 cumulative probability showed the reasonable values when these data were compared with the reference data. So that the model was proved as a good corrosion model m the neutral low dissolved oxygen environment.
Imai, Jun*
JNC TJ8400 2000-008, 196 Pages, 2000/02
The objective of this research is to make clear long-term alteration processes of bentonite contacting with concrete under a repository condition for radioactive waste. The Uzu tunnel in yamagata prefecture in Japan, constructed during the term of December of 1963 to July 1967, was selected as an appropriate natural analogue: the tunnel wall was made of portland cement and which has been contacting with a bentonite bed during  32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na
32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na -type and it changed to Ca
-type and it changed to Ca -type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca
-type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO
leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO  Al
Al O
O
 3CaSO
3CaSO 4
4  32H
32H O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.